In the medical field, ergothioneine can be used orally to prevent dementia, treat cancer, improve cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, central nervous system diseases, etc. It can also be used topically to treat skin and inflammatory diseases, with significant efficacy in treating skin diseases.
Prevention of Dementia
Oral intake of ergothioneine is beneficial to the brain and helps prevent dementia. A 9-year follow-up study by the National University of Singapore on 496 participants found that plasma levels of ergothioneine were significantly lower in dementia patients compared to normal individuals.
Improvement of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases
Ergothioneine reduces oxidative stress, which may lead to decreased antioxidant capacity, resulting in neurological and cardiovascular diseases. Studies have shown that plasma levels of ergothioneine are significantly decreased in patients with hypertension, diabetes, or cardiovascular diseases.
Improvement of Central Nervous System Diseases
Research indicates that ergothioneine, upon absorption, exhibits antidepressant effects through anti-inflammatory mechanisms in the central and/or peripheral nervous systems.
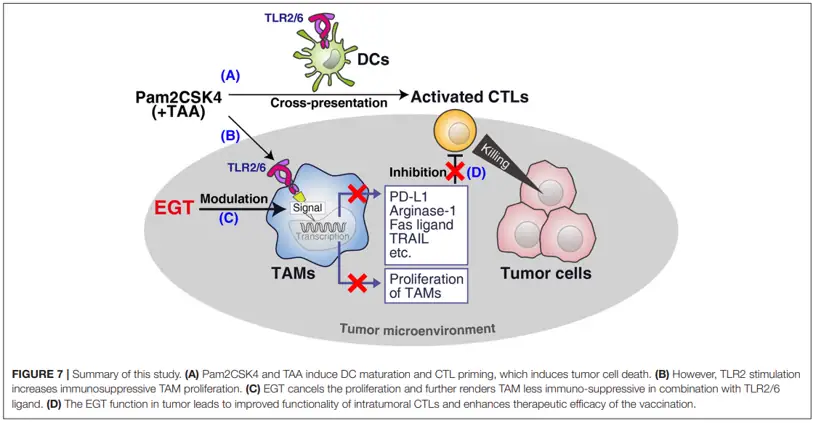
Treatment of Cancer
Ergothioneine can promote adjuvant vaccine immunotherapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Studies have shown that EGT still fails to reduce reactive oxygen species in CD45− tumor cells, which contributes to cancer treatment. The established safety of ergothioneine further confirms its efficacy in cancer patients.
Improving Eye Disorders
Ergothioneine helps protect the eyes from oxidative damage, and low levels of ergothioneine may lead to eye diseases. Research from the National University of Singapore indicates that the level of ergothioneine in the human eye lens decreases significantly with the severity of cataracts. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a major cause of irreversible blindness, and its pathogenic mechanism involves oxidative damage and immune dysregulation, indicating that ergothioneine has a protective effect against this disease.